- Syslog submits a message to the Syslog facility. It does this by writing to the Unix domain socket /dev/log. Syslog submits the message with the facility and priority indicated by facilitypriority. The macro LOGMAKEPRI generates a facility/priority from a facility and a.
- Here’s how to create UDP syslog messages via nc, netcat: echo ‘ sourcehost message text’ nc -v -u -w 0 localhost 514 Replace localhost with the syslog server, of course. “sourcehost” is a string identifying the source; can be anything.
Nc Syslog
In computing, syslog/ˈsɪslɒɡ/ is a standard for message logging. It allows separation of the software that generates messages, the system that stores them, and the software that reports and analyzes them. Each message is labeled with a facility code, indicating the software type generating the message, and assigned a severity level.
Computer system designers may use syslog for system management and security auditing as well as general informational, analysis, and debugging messages. A wide variety of devices, such as printers, routers, and message receivers across many platforms use the syslog standard. This permits the consolidation of logging data from different types of systems in a central repository. Implementations of syslog exist for many operating systems.
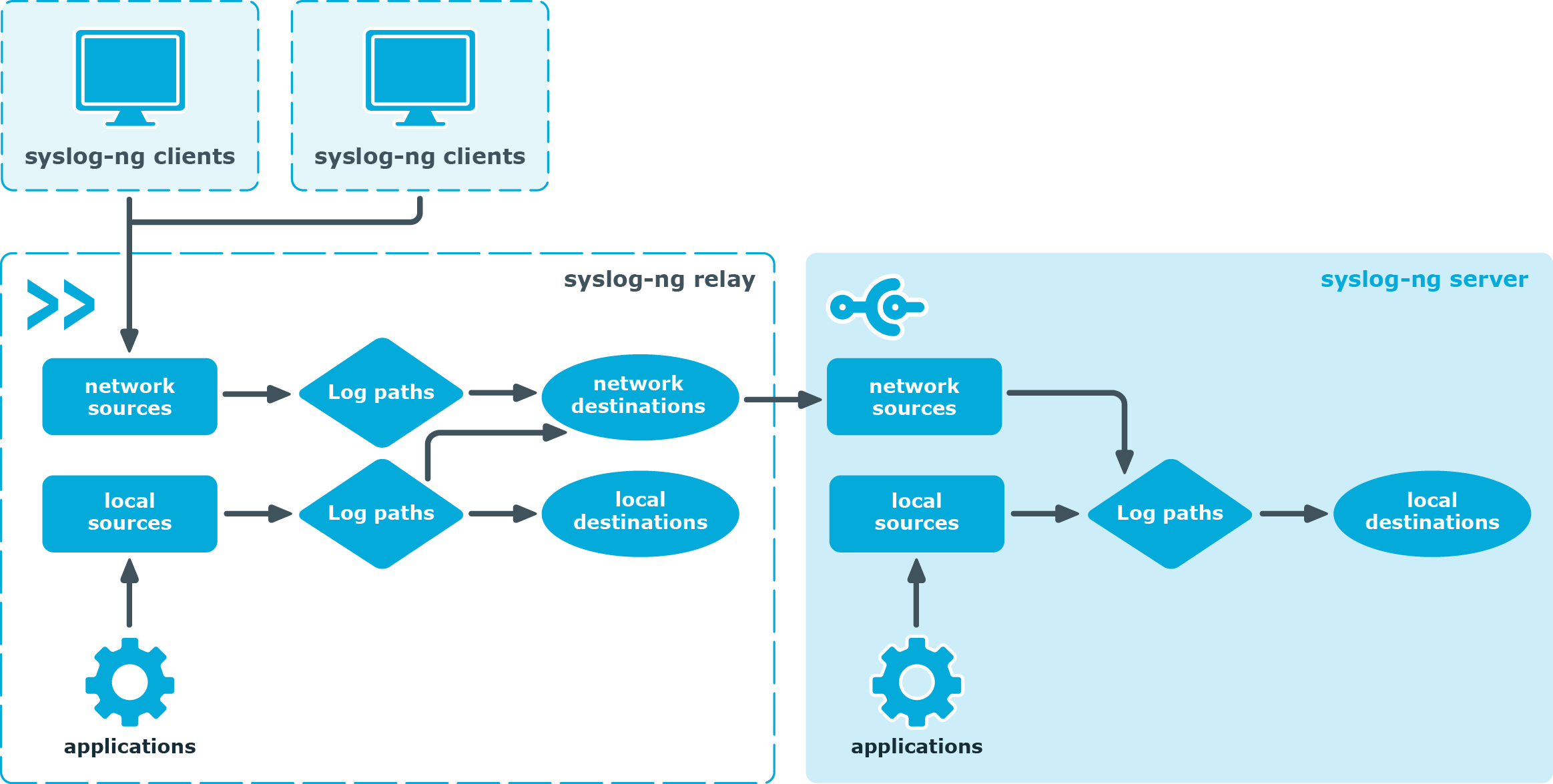
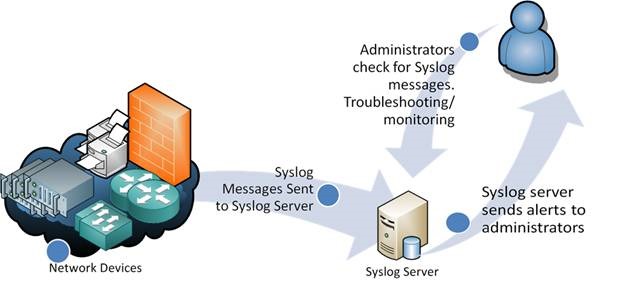
When operating over a network, syslog uses a client-server architecture where a syslog server listens for and logs messages coming from clients.
History[edit]
Syslog was developed in the 1980s by Eric Allman as part of the Sendmail project.[1] It was readily adopted by other applications and has since become the standard logging solution on Unix-like systems. A variety of implementations also exist on other operating systems and it is commonly found in network devices, such as routers.
Syslog originally functioned as a de facto standard, without any authoritative published specification, and many implementations existed, some of which were incompatible. The Internet Engineering Task Force documented the status quo in RFC 3164. It was standardized by RFC 5424.[2]
Various companies have attempted to claim patents for specific aspects of syslog implementations.[3][4] This has had little effect on the use and standardization of the protocol.[citation needed]
Message components[edit]
The information provided by the originator of a syslog message includes the facility code and the severity level. The syslog software adds information to the information header before passing the entry to the syslog receiver. Such components include an originator process ID, a timestamp, and the hostname or IP address of the device.
Another free syslog server software, WhatsUp Gold Syslog Server is a straightforward way to manage your syslog needs. It monitors syslog messages and provides real-time views into message data as well as filters to help you sort through the approximately 6,000,000 messages it can process per hour. $ nc -zv 192.168.1.15 22 In the command above, the flag:-z – sets nc to simply scan for listening daemons, without actually sending any data to them.-v – enables verbose mode. The next command will check if ports 80, 22 and 21 are open on the remote host 192.168.5.10 (we can use the hostname as well): nc -zv 192.168.56.10 80 22 21. Basically run a telnet from the CLI of the ESXi host to your syslog server on port 514 (if you use the default one) 4) The syslog server allows all inbound UDP traffic to port 514 Dozens of hosts use it successfully.
Facility[edit]
A facility code is used to specify the type of program that is logging the message. Messages with different facilities may be handled differently.[5] The list of facilities available is defined by the standard:[2]:9
| Facility code | Keyword | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | kern | Kernel messages |
| 1 | user | User-level messages |
| 2 | Mail system | |
| 3 | daemon | System daemons |
| 4 | auth | Security/authentication messages |
| 5 | syslog | Messages generated internally by syslogd |
| 6 | lpr | Line printer subsystem |
| 7 | news | Network news subsystem |
| 8 | uucp | UUCP subsystem |
| 9 | cron | Clock daemon |
| 10 | authpriv | Security/authentication messages |
| 11 | ftp | FTP daemon |
| 12 | ntp | NTP subsystem |
| 13 | security | Log audit |
| 14 | console | Log alert |
| 15 | solaris-cron | Scheduling daemon |
| 16–23 | local0 – local7 | Locally used facilities |
The mapping between facility code and keyword is not uniform in different operating systems and syslog implementations.[6]

Severity level[edit]
The list of severities is also defined by the standard:[2]:10
| Value | Severity | Keyword | Deprecated keywords | Description | Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Emergency | emerg | panic[7] | System is unusable | A panic condition.[8] |
| 1 | Alert | alert | Action must be taken immediately | A condition that should be corrected immediately, such as a corrupted system database.[8] | |
| 2 | Critical | crit | Critical conditions | Hard device errors.[8] | |
| 3 | Error | err | error[7] | Error conditions | |
| 4 | Warning | warning | warn[7] | Warning conditions | |
| 5 | Notice | notice | Normal but significant conditions | Conditions that are not error conditions, but that may require special handling.[8] | |
| 6 | Informational | info | Informational messages | ||
| 7 | Debug | debug | Debug-level messages | Messages that contain information normally of use only when debugging a program.[8] |
The meaning of severity levels other than Emergency and Debug are relative to the application. For example, if the purpose of the system is to process transactions to update customer account balance information, an error in the final step should be assigned Alert level. However, an error occurring in an attempt to display the ZIP code of the customer may be assigned Error or even Warning level.
The server process which handles display of messages usually includes all lower (more severe) levels when display of less severe levels is requested. That is, if messages are separated by individual severity, a Warning level entry will also be included when filtering for Notice, Info and Debug messages.
Message[edit]
In RFC 3164, the message component (known as MSG) was specified as having these fields: TAG, which should be the name of the program or process that generated the message, and CONTENT which contains the details of the message.
Described in RFC 5424,[9] 'MSG is what was called CONTENT in RFC 3164. The TAG is now part of the header, but not as a single field. The TAG has been split into APP-NAME, PROCID, and MSGID. This does not totally resemble the usage of TAG, but provides the same functionality for most of the cases.' Popular syslog tools such as Rsyslog conform to this new standard.
The content field should be encoded in a UTF-8 character set and octet values in the traditional ASCII control character range should be avoided.
Logger[edit]
Generated log messages may be directed to various destinations including console, files, remote syslog servers, or relays. Most implementations provide a command line utility, often called logger, as well as a software library, to send messages to the log.
To display and monitor the collected logs one needs to use a client application or access the log file directly on the system. The basic command line tools are tail and grep. The log servers can be configured to send the logs over the network (in addition to the local files). Some implementations include reporting programs for filtering and displaying of syslog messages.
Network protocol[edit]
When operating over a network, syslog uses a client-server architecture where the server listens on a well-known or registered port for protocol requests from clients. Historically the most common transport layer protocol for network logging has been User Datagram Protocol (UDP), with the server listening on port 514. As UDP lacks congestion control mechanisms, support for Transport Layer Security is required in implementations and recommended for general use[10] on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 6514.[11]
Limitations[edit]
Netcat Nc Syslog
Since each process, application, and operating system was written independently, there is little uniformity to the payload of the log message. For this reason, no assumption is made about its formatting or contents. A syslog message is formatted (RFC 5424 gives the Augmented Backus–Naur form (ABNF) definition), but its MSG field is not.
The network protocol is simplex communication, with no means of acknowledging the delivery to the originator.
Outlook[edit]
Various groups are working on draft standards detailing the use of syslog for more than just network and security event logging, such as its proposed application within the healthcare environment.[12]
Regulations, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and many others, require organizations to implement comprehensive security measures, which often include collecting and analyzing logs from many different sources. The syslog format has proven effective in consolidating logs, as there are many open-source and proprietary tools for reporting and analysis of these logs. Utilities exist for conversion from Windows Event Log and other log formats to syslog.
Managed Security Service Providers attempt to apply analytical techniques and artificial intelligence algorithms to detect patterns and alert customers to problems.
Internet standard documents[edit]
The Syslog protocol is defined by Request for Comments (RFC) documents published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (Internet standards). The following is a list of RFCs that define the syslog protocol:[13]
- The BSD syslog Protocol. RFC3164. (obsoleted by The Syslog Protocol. RFC5424.)
- Reliable Delivery for syslog. RFC3195.
- The Syslog Protocol. RFC5424.
- TLS Transport Mapping for Syslog. RFC5425.
- Transmission of Syslog Messages over UDP. RFC5426.
- Textual Conventions for Syslog Management. RFC5427.
- Signed Syslog Messages. RFC5848.
- Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) Transport Mapping for Syslog. RFC6012.
- Transmission of Syslog Messages over TCP. RFC6587.
See also[edit]
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
References[edit]
- ^'Eric Allman'. Internet Hall of Fame. Retrieved 2017-10-30.
- ^ abcGerhards, Rainer. The Syslog Protocol. doi:10.17487/RFC5424. RFC5424.
- ^'LXer: Patent jeopardizes IETF syslog standard'.
- ^'IETF IPR disclosure on HUAWEI's patent claims'.
- ^'Syslog Facility'. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^'The Ins and Outs of System Logging Using Syslog'. SANS Institute.
- ^ abc'syslog.conf(5) - Linux man page'. Retrieved 2017-03-29.
- ^ abcde'closelog, openlog, setlogmask, syslog - control system log'. Retrieved 2017-03-29.
- ^Gerhards, Rainer (March 2009). 'RFC 5424 - The Syslog Protocol'.
This document describes a layered architecture for syslog. The goal of this architecture is to separate message content from message transport while enabling easy extensibility for each layer.
- ^'RFC 5424 - The Syslog Protocol'.
- ^'RFC 5425 - TLS Transport Mapping for Syslog'.
- ^'ATNA + SYSLOG is good enough'. Healthcare Exchange Standards. Retrieved 2018-06-06.
- ^'Security Issues in Network Event Logging (syslog)'. IETF.
External links[edit]
- SANS Institute: 'The Ins and Outs of System Logging Using Syslog' (white paper)
- National Institute of Standards and Technology: 'Guide to Computer Security Log Management' (Special Publication 800-92) (white paper)
Syslog: Sending log from remote servers to syslog daemon
July 23rd, 2008 mysurface Posted in Admin, logger, nc, rsyslogd, syslogd, tail | Hits: 307453 | 8 Comments »
syslog is a standard for logging service in Linux, it usually run as daemon like syslogd or rsyslogd. Syslog daemon will be forward and store logs in /var/log directory, you may configure it to store at separate location if you want. (we will look into it later). And there is a major file that store majority of logs, which is messages. Therefore, you may want to monitor linux messages logs by tailing /var/log/message.
Logs entry may come from various services, applications, kernel as well as remote servers if you enabled your syslog daemon to accept remote logs submissions. Syslog protocol is now standardized within the Syslog working group of the IETF, and it is been defines in RFC 3164.
Rsyslog is an enhanced multi-threaded syslogd with a focus on security and reliability. I think newer linux distro already replace syslogd with rsyslogd. For more information you can check out the wikipedia.
In this post, I briefly explain the facility and log levels of syslog protocol, how to configure syslogd as well as rsyslogd to accept logs from remote and also how to send logs remotely.
Syslog categories logs into PRI which constructed by facility and severity/priority/log levels.
Facility defines the source of the log entries, what kind of services that send this logs. Lets look at Facility info that extracted from RFC 3164, each facility was been assign a numeric code.
Severity is the log levels that defines how critical of the log entries, from 0 – 7, 0 indicates the most critical and 7 is for debugging purpose.
PRI is a unique values constructed by facility and severity where severity takes 3 LSB (least significant bits) append with facility start from bit 4.
<< indicates left shift which I borrow it from c++ programming language, when I do left shift N its like multiply with 2^N(two to the power of N). In this context, PRI formula can be written as
PRI is important when you wanna send message to syslog, the default message PRI is user(1).notice(5) which the PRI value is 8 + 5 = 13. Meaning if you do not specified the PRI value, it will be treated as 13.
For common Linux distro, syslogd or rsyslogd should be started before you login to your system, you can verify that with ps.
Usually syslogd comes with distro does not configured to accept remote messages, unless -r is specified.
How to enable syslogd to accept remote message?
syslog will listening to UDP port 514 for messages sent remotely, but if your distro running rsyslogd, you can listen to TCP port and you may also need to specify the port number.
Different Linux distro may have different ways of configuration, let say if you are using Red hat based distro, your syslogd and rsyslogd configuration will be at /etc/sysconfig/syslog or /etc/sysconfig/rsyslog.
For the case of rsyslogd, change the SYSLOGD_OPTIONS in /etc/sysconfig/rsyslog from SYSLOGD_OPTIONS=”-m 0″ to SYSLOGD_OPTIONS=”-m 0 -r514″ for UDP and SYSLOGD_OPTIONS=”-m 0 -t514″ for TCP. For the case of syslogd, change it to SYSLOGD_OPTIONS=”-m 0 -r”.
After that, restart your syslog or rsyslog services, In Fedora or Red Hat, you may do this with root permission.
Or you can just kill the syslogd process and start manually from console for testing.
Syslog Configurations
syslog daemon includes a configuration files to specified which logs to keep and append it to which file based on the PRI stated above.
Below are the sample of /etc/rsyslog.conf
You defines what messages goes to what file like this:
For example:
The line above indicates that, when I get syslog message with facility user and severity notice, it will be append to file /var/log/user.notice.
For more info, please check out here.
How to send message to syslogd?
For sending locally, we can use the logger command. Before you send the message to syslog, lets tail the message log.
Now send “hello world” with logger.
It will appear in /var/log/messages as well as /var/log/user.notice if you have configure syslog.conf to forward user.notice messages to /var/log/user.notice. This proves that the default message’s PRI is user.notice. You may assign different PRI value to logger. For example if I wanna send message with PRI = user.info:
How to send log message to remote server?
Unfortunately, you can’t send through logger. But you can manually send a plain text UDP package to remote servers that listening on UDP port 514. With the help of netcat(nc), we can send the message to remote syslogd as simple as logger command.
To assign your message a PRI, you need to specified PRI’s value in numeric.
User.Info’s PRI value is:
(1 << 3 ) + 6 = 8 + 6 = 14. ( refers back the numerical code of facility and severity )
If your rsyslogd are listening to TCP port, just ignore -w0 and -u:
Related PostsBTTB: looping for shell script under embedded linux

